
Perform web application testing to ensure comprehensive functionality, security, and user experience. Explore diverse types, tools, and cutting-edge approaches.
Web application testing is a software testing approach designed for evaluating applications hosted on the web. This web application testing method involves functionality, security, and another application interface to ensure they are effective and reliable.
The primary purpose of web application testing is to fix any issues and vulnerabilities in the web application before it is released on the market. With this test, you can ensure the web application meets all the end-user requirements and provides a high-quality experience. However, it is essential to conduct web application testing with accuracy.
In this tutorial, we will look deep into the types and approaches of web application testing, how it differs from mobile app testing, the tools that are used to perform web application testing, and how you can make use of the cloud-based platform to leverage the capabilities of web application testing.
Let us get started by first understanding what a web application is.
Web applications are a big part of our daily lives and will become even more critical in 2023 and beyond. A web app is just software you use on a web browser or phone. It needs the Internet to work and runs on a web server.
Before we cover the details of web application testing, it is essential to know the basics of web application in the following section.
In this section, we will look into the definition of a web application, technologies used for developing web applications, functionality, and more sequentially.
Web applications are programs that reside on remote servers and allow users to access them via web browsers. In simple terms, web applications are software programs/software modules that operate through a web browser, using various web technologies to carry out tasks on the internet.

Web applications commonly use specialized computer programs to manage and store information on the Internet. Generally, these web application programs are divided into two types of scripts that run simultaneously.
To make all this work, a web application needs both a web server and an application server. A web server is a software element that responds to client requests by providing static data, such as images, files, and text.
An application server enhances the web server's response by adding business logic to process and compute the requested data. These servers receive and manage client requests and perform the tasks the user requests.
When loading web pages or websites, HTML is compiled into a Document Object Model (DOM) that shows its structure. CSS is a style description framework mainly used to style and format visual elements of web applications. Further, JavaScript is a high-level scripting language upon which all dynamic behavior of web applications is scripted and executed.
Besides the above technologies, JavaScript frameworks like Angular, React, and Vue are used as they give ready-to-use tools and libraries. This simplifies the process of making a complex user interface.
CSS Preprocessors like LESS and SASS allow writing and organizing CSS code efficiently. It gives features like variables, mixins, and nesting, allowing developers to maintain a reusable style across web applications. Also, the HTML templating simplifies generating dynamic HTML content.
To summarize, web applications use server-side and client-side scripting. Organizations or individuals can communicate through online forms, forums, shopping carts, and more. They also allow users to create and share documents or information. With web applications, people can collaborate on projects even if they're not in the same place.
Now, let us learn about different types of web applications. It will help you get an idea of testing these applications.
Before we begin testing web applications, it's essential to know the different types of web applications to help you understand what testing approach can be applied for which kind of web application.
Some of the web application types are listed below.
Dynamic web apps can be divided into two types:
If you wish to know more about the other types of web and mobile apps, explore this blog on different mobile apps and get valuable insights for expanding your basic knowledge in this domain.
Note : Run web application tests across various browsers and devices. Try LambdaTest Now!
We use web applications for online shopping, social media, banking, entertainment, etc. However, any bug or error in the web applications can interfere with their usability and function, making them low-quality.
But have you ever wondered how these applications are tested to ensure they work flawlessly and provide a great user experience? That's where web application testing comes in. It ensures that your web applications work correctly when rendered across multiple browsers, devices, and operating systems combinations.
Web application testing evaluates and assesses all aspects of a web application’s functionality, like detecting bugs with usability, compatibility, security, and performance. This testing practice ensures the quality of the web application and that it is working as per the end-user requirements.
It systematically checks and verifies the web application's components and features to ensure a positive user experience. This systematic approach performs various tests to detect issues, bugs, and vulnerabilities affecting web applications' performance and security.
Some of those tests are functional testing, performance testing, security testing, etc. The QA teams mainly conduct it by simulating real-world scenarios and user interactions to verify the web application’s behavior and ensure its reliability.
The main goal of web application testing is to uncover and rectify any issues and weaknesses in the web application and lower the incidence of data breaches or system failure. With web application testing, developers can check that the developed web application meets the required standards and delivers a seamless user experience.
Testing a website is crucial and should be done after developing a new feature because we can only guarantee bug-free software delivery with proper web app testing. Website testing is essential to identify and report any defects in the product. If testers don't conduct thorough testing, there's a high chance that end users will find issues, leading to customer dissatisfaction.
Failing to conduct rigorous tests on web applications increases the risk of defects and the likelihood of losing customers. Compromising software quality negatively impacts the organization's reputation. Website testing plays a vital role in ensuring high-quality software. Through web page testing, developers can confirm that the product doesn't have critical flaws.
Delivering bug-free software to the market attracts new customers, contributing to revenue generation.
A report by Statista says that the global market for making these web apps will be worth $167 billion in 2023. They expect the money it makes to grow by 7.04% each year until 2028, reaching a total of $234.70 billion.
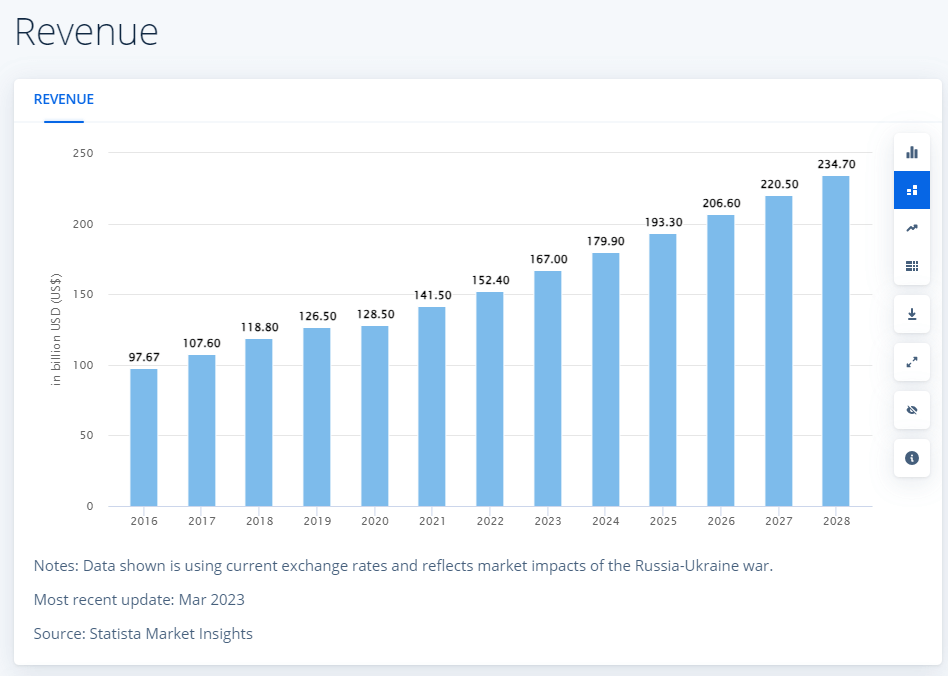
Source
Now that we have seen what web application testing is and why it is important let us see some of the benefits in the following section.
To resolve usability issues, you can use usability testing methods that will give you a complete understanding of usability testing and its methods to help you achieve quality and better user experience.
Addressing usability issues can be achieved by implementing specific usability testing methods defined in a comprehensive guide. Each method mentioned in this guide provides detailed information on conducting usability testing and offers insights into resolving usability issues effectively.
We learned about web application testing, its benefits, and why it is essential. In the following section, let us understand how web application testing differs from mobile application testing.
Testing web and mobile apps is essential to ensure the software works well. Web apps work on different devices using a browser, while mobile apps are made for smartphones and tablets. Both testing processes have their things to consider to ensure everything runs smoothly on the web and mobile.
At first glance, testing web applications can be found similar to performing mobile app testing. But you will learn about its significant differences when you delve into its concept. Here are some common differences between them based on the aspects.
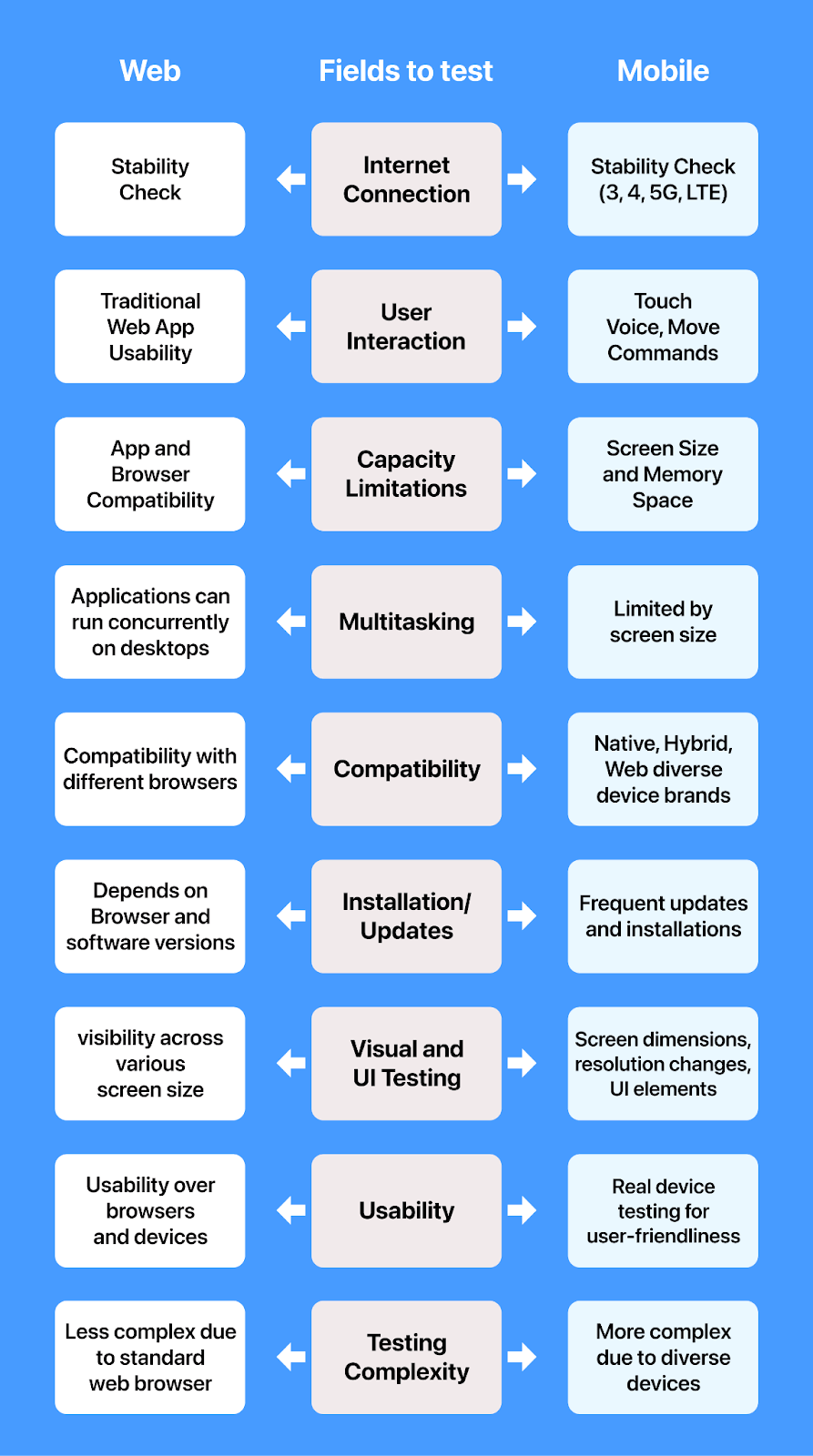
| Aspects | Web Application Testing | Mobile Application testing |
|---|---|---|
| Internet Connection | Focus on stability and speed of Internet connection. | Test different network types (3G, 4G, 5G, Wi-Fi) and speeds |
| User Interaction | Primarily involves keyboard and mouse interactions. | Test touch gestures, voice commands, and device sensors. |
| Capacity Limitations | Focus on compatibility with various browsers and devices. | Consider device-specific factors: battery, RAM, SSD, and screen. |
| Multitasking | Concurrent handling of multiple user sessions | This involves managing various processes concurrently, including background tasks and user interactions. |
| Compatibility | Compatibility across browsers, OS, and screen sizes. | Compatibility across devices, OS (iOS, Android), and screen resolutions. |
| Installation/Updates | No installation is required; updates happen on the server. | It requires installation from app stores, and updates are managed through app store platforms. |
| Visual and UI Testing | Ensures visibility and accessibility across various screen sizes. | Screen dimensions, resolution changes, UI elements. |
| Usability | Focus on usability across different browsers and devices. | Involves real device testing for user-friendliness. |
| Testing Complexity | It is, generally, less complex as it involves a standard web browser. | It is more complicated due to diverse devices, OS versions, and types. |
Web and mobile applications are often interconnected, leading testers to use shared testing methodologies. To address this, a robust test management platform becomes essential for creating a unified testing strategy involving common workflows, resources, and scenarios relevant to web and mobile app testing.
The web application testing life cycle is a structured approach to testing the web application’s reliability and quality. It follows a series of phases that help identify defects, ensure functionality, and assess web application performance. These are the different phases involved in web application testing.

The phases of web application testing mentioned above help ensure that web applications are thoroughly tested before being deployed to production. These phases are executed by two approaches: manual and automation. We will get into more detail on the approaches mentioned in further sections.
Now that we know the phases of web application testing, let us look into the web application testing scenarios in the following section below.
Web application testing is performed in different conditions and scenarios. When you start with a web application, a test scenario should be kept in mind so that all the features and aspects of web applications are tested.
These scenarios are essential for ensuring the web application's quality, functionality, and usability. Some of those scenarios are.
Web application testing includes different testing techniques and different forms of testing. Including all tests at different phases of web application testing is crucial. Here are the testing techniques that should be followed while performing web application testing.
This type of testing ensures that all web application functionalities are verified and specification requirements are met. Such tests are performed using test cases that confirm the functionality of each web application component.
Functional testing is carried out through different levels of tests, which are discussed below:
Developers do unit testing to test each module or unit of the web application. Generally, the developers check the expected working of each code unit and help in the early detection of bugs in the web application development process.
Integration testing is functional testing that involves testing the working of different code units together. In other words, in this level of testing, various components are integrated and tested by the developers and testers. It can be executed using black box testing and white box testing techniques.
System testing is where the testing team tests the whole web application. It helps validate all end-user requirements before it is released to them. Here, all the components of web applications and their interactions are tested.
The main goal of regression testing is to ensure that the alterations of codes do not disrupt existing features or introduce new bugs to the application, maintaining the overall stability and reliability of the software.
Acceptance testing is the final testing level, where the final test is conducted to ensure that the web application meets the end-users requirements. End-users mainly execute it to ensure all the required web application features are implemented correctly.
Following is the checklist to be considered while performing functional testing:
Non-functional testing in web applications focuses on evaluating aspects other than functionality. It examines performance, usability, security, reliability, and scalability. This type of testing assesses how well the web application performs under different conditions, such as high user loads or varying network speeds. It also verifies if the application meets industry standards and compliance requirements.
Non-functional testing ensures the web application delivers a seamless user experience, performs optimally, and meets the expected non-functional requirements to meet user expectations and business needs.
UI testing aims to assess the web application's user interface. It checks if the interface aligns with industry standards regarding effectiveness and user-friendliness. Following global conventions and web standards is crucial while developing a web application.
During UI testing, testers pay attention to specific critical factors such as correct navigation, a site map for easy browsing, and avoiding overcrowded content that can confuse end-users. The goal is to create a straightforward, user-friendly interface that enhances the user experience.
Usability testing includes real individuals interacting with a website, app, or product, with their behavior and reactions observed. This testing is crucial to ensure the application provides users with an effective, efficient, and enjoyable experience.
Here are different types of usability testing used to test web applications:
Performance testing allows you to evaluate how well a web application can perform in different scenarios for various criteria like response time and interoperability. It involves additional tests, such as stress and load testing, to assess the application's functionality under different testing scenarios.
Several types of performance testing can be used for web applications, including
Following is the checklist to be considered while performing performance testing:
Compatibility Testing tests web applications to ensure they work and function seamlessly across different web browsers, OS, and hardware platforms. Such a test is mainly performed to check and verify whether the web application meets user experience on diverse types of devices and environments.
Different types of compatibility testing include the following:
Following is the checklist to be considered while performing compatibility testing:
This test type finds any security flaws in the web application and ensures it is safe and secure against online threats. The main goal of a security test is to identify any security risk and vulnerability and fix it promptly before it is released on the market.
Different types of security testing include the following.
Following is the checklist to be considered while performing security testing:
Web application testing, being a subset of software testing, enables developers to verify whether there are any bugs and errors in the application. Primarily, it is executed by two different approaches:
Manual testing of web applications is needed when in-depth testing is required. It involves executing test cases manually without relying on automated testing tools. They carefully examine every aspect of the application to identify any flaw affecting its usability.
When manually testing a web application, testers simulate real-world usage scenarios. They click buttons, fill out forms, navigate through different pages, and perform various actions to ensure everything functions smoothly. With this, an organization can validate its web application and assess important factors like accuracy, completeness, user-friendliness, efficiency, and more. It is often the initial step in creating user-friendly and intuitive interfaces.
Web application testing using an automated approach involves testing with automation testing frameworks with minimal human effort requirements. Technically, automation testing of web applications involves using automated tools and scripts to execute test cases and validate the web application's functionality, performance, and usability.
These scripts simulate user actions like clicking buttons, filling out forms, and navigating different pages. To perform automation testing of web applications, testers utilize specialized testing frameworks and tools such as Selenium, Cypress, or Playwright. These tools provide features like recording and playback, script creation, element identification, and reporting capabilities.
Choosing the right automation testing tool can be tricky, as each tool has challenges. Testers might face issues like missing features, trouble with parallel testing, or difficulties in visual testing. Not all tools cover everything a tester needs. To tackle these challenges, a cloud-based platform like LambdaTest can be helpful.
However, it's important to note that not all tests can or should be automated. Automation testing is most effective for repetitive tasks, large-scale projects, and scenarios where a high level of accuracy is required. Certain aspects of testing, such as usability evaluation or exploratory testing, still benefit from manual intervention and human judgment.
Now that we have learned the different types of testing and approaches that web applications follow, let us see the tool that can help enhance and scale the capabilities of web application testing in the following section.
Web application testing using the automation approach saves lots of time in the testing process. It ensures the fixation of errors and bugs at an early stage. The use of automation testing tools can help in accomplishing this. Here are some tools that can be leveraged to automate the web application testing process.
LambdaTest is an AI-powered test orchestration and execution platform enabling you to run manual and automation tests over web applications, offering access to 3000+ real devices, browsers, and OS combinations.
Learn how to run automation tests effortlessly using LambdaTest with this quick overview.
Selenium is an open-source test automation tool widely used for web application testing. It provides automation capabilities across multiple operating systems, such as Windows, Mac, and Linux, and popular web browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, and Edge. Selenium allows testers to write test scripts in various programming languages like Java, Python, and C#, making it flexible and adaptable for different testing needs.
As we all know, Selenium 3 had a significant transition as it implemented WebDriver independently. However, this evolution has progressed to Selenium 4, with W3C WebDriver specification.
To know more about the new features and improvements Selenium 4 holds, explore the detailed guide on Selenium 4 with examples for better understanding. However, if you are still using Selenium 3, consider upgrading from Selenium 3 to Selenium 4.
Watch the complete video tutorial on Selenium 4, get valuable insights, and enhance your automation testing experience.
It is an open-source testing framework for browser automation and testing of web applications. It supports multiple web browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, etc. Playwright offers APIs for automating web interactions and performing tests in various programming languages such as JavaScript, Python, etc.
It focuses on providing reliable cross-browser testing ability and supports headless and UI testing scenarios.
Subscribe to the LambdaTest YouTube channel when you want to catch up with the latest news on automated browser testing, automated UI testing, and more.
Cypress is an open-source end-to-end testing tool designed to test web applications built on JavaScript frameworks. It allows QA engineers to write tests using JavaScript, providing real-time execution and simultaneous viewing of test cases being created.
It offers a rich set of features for easier debugging, time-traveling, and stubbing network requests, making it popular among developers and testers for its simplicity and efficiency.
To know more about Cypress and some valuable tips, watch the complete Cypress video tutorial and make your automation experience easy.
It is another popular open-source tool for browser automation developed by Google. It allows developers and testers to control and interact with web pages programmatically. Puppeteer provides a high-level API for automating tasks like generating screenshots, PDFs, and crawling pages.
It supports Chrome and other Chromium-based browsers and is commonly used for web scraping, testing, and generating performance reports.
Selecting the right automation testing tool is essential for QA teams to match the specific needs of their projects. Check out this comprehensive guide on choosing the best automation testing tool for your project needs. This guide provides valuable insights to help QA teams make informed decisions and encourage testers to select the most suitable one for their requirements.
When you begin web application testing, certain factors should be considered to ensure successful test completion. Here are six key elements to look for in web app testing.
Evaluate HTML page interactions, TCP/IP communications, and JavaScript.
Validate applications for CGI Scripts, database interfaces, dynamic page generators, etc.
Test web applications across browsers, operating systems, localization, and globalization:
Test web URLs for proper functioning
Check for typos, grammar mistakes, and incorrect punctuation
Map old pages to new pages to avoid content loss during the transition
If the web application undergoes any updates, redesigns, or restructuring, ensure that old pages are correctly mapped or redirected to new ones. This helps prevent users from encountering broken links or losing access to valuable content during the transition.
When you have considered all the crucial factors in testing web applications next, you have to ensure that they are end-to-end tested. This will provide complete information on the quality of web applications and identify and fix all the bugs and errors. Here are some other reasons why end-to-end testing of web applications should be addressed.
Web application testing requires some preparation before digging into the actual testing process. This will help you get all aspects of testing web applications in one place and pipeline to have a systematic approach to the testing process.
The initiation of web application testing needs some preparation, ensuring the testing process is aligned with the project objectives and the test environment is accurately set up. A straightforward test strategy is in place to guide the testing efforts. Here are the steps to be followed for preparing for web application testing:
When starting a web application test, you must first be clear about its test objective and goal. For example, it is essential to identify the exact areas, key functionalities, and environments that must be tested. This will allow you to create compelling test cases and ensure complete test coverage.
Set up the test environment that closely resembles the production environment in which the web application will be deployed. This involves configuring the hardware, software, networks, databases, and other components required to replicate the deployment environment. A well-prepared test environment helps conduct realistic tests and identify potential issues early on.
Develop a test strategy that outlines the approach, methodologies, and techniques to be employed during the testing process.
This includes determining the types of tests to be performed (e.g., functional, performance, security), selecting appropriate testing tools and frameworks, establishing test timelines and milestones, and defining roles and responsibilities within the testing team. A well-defined test strategy ensures a systematic and structured approach to web application testing.
After preparing for the test and knowing what and how to test, you must move to the actual testing process. Web app testing can be performed on a local computer or in the cloud, each with advantages and disadvantages.
Testing on a local machine provides greater control over the testing environment. Teams can customize the infrastructure and tools to meet their requirements, resulting in faster testing cycles without network latency. As a result, more resources will be required to help scale up to more significant scenarios.
In contrast, cloud-based testing offers unlimited resources and scalability without hardware limitations. Additionally, this method is cost-effective since teams pay only for the resources they need.
The following section will dive deep into how to test web applications on the cloud platform.
Web application testing in the cloud means that web applications are tested on cloud-based servers and resources. But why test on the cloud even though we have so many automation testing frameworks and tools in the market that allow web app testing?
The cloud-based platform offers several benefits that ease your web application testing process. You can scale up and down the testing environment according to the testing needs. You can access the web application from anywhere with an Internet connection, facilitating remote collaboration and enabling teams to work seamlessly across different locations.
The focus on web applications has surged the testing tools and platforms standard. You can leverage the true capability of web application testing by performing the test on a cloud-based platform. In this case, we are using LambdaTest as a cloud-based platform.
Before testing on the cloud platform, we must do some setup tasks. This includes signing up on the cloud platform, configuring capabilities, and other actions discussed below.
To better understand the platform, we will run real-time browser testing on cloud infrastructure, enabling compatibility checking across different browser and operating system combinations.
This section will explore the effective utilization of cloud-based platforms for manual testing on desktops and virtual mobile.
Here are the steps to follow to perform Real-Time testing.
Step 1: Create a LambdaTest account and log in. Once logged in, you can see the LambdaTest Dashboard as shown below.
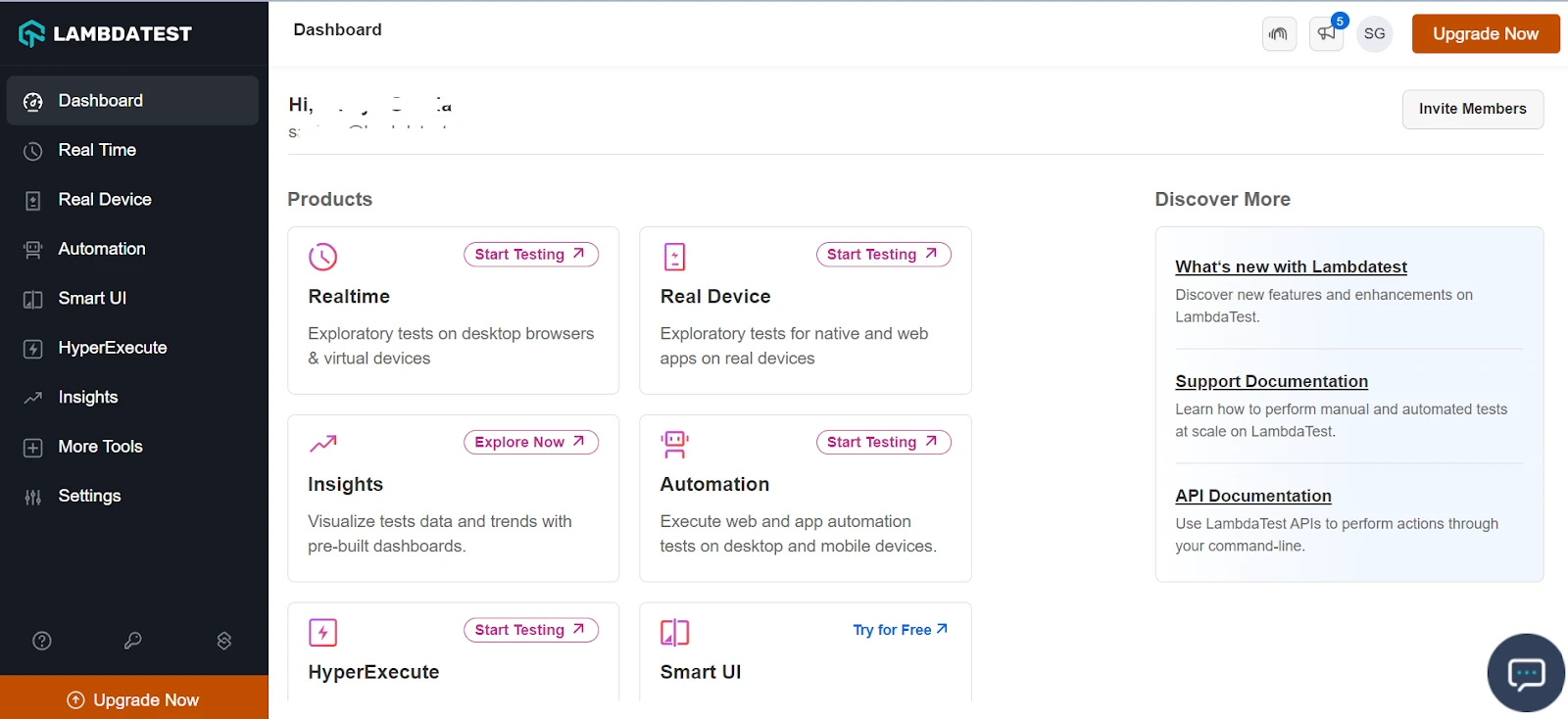
Step 2: Click Real Time from the left side of the menu.

Step 3: Select Desktop from the left menu.
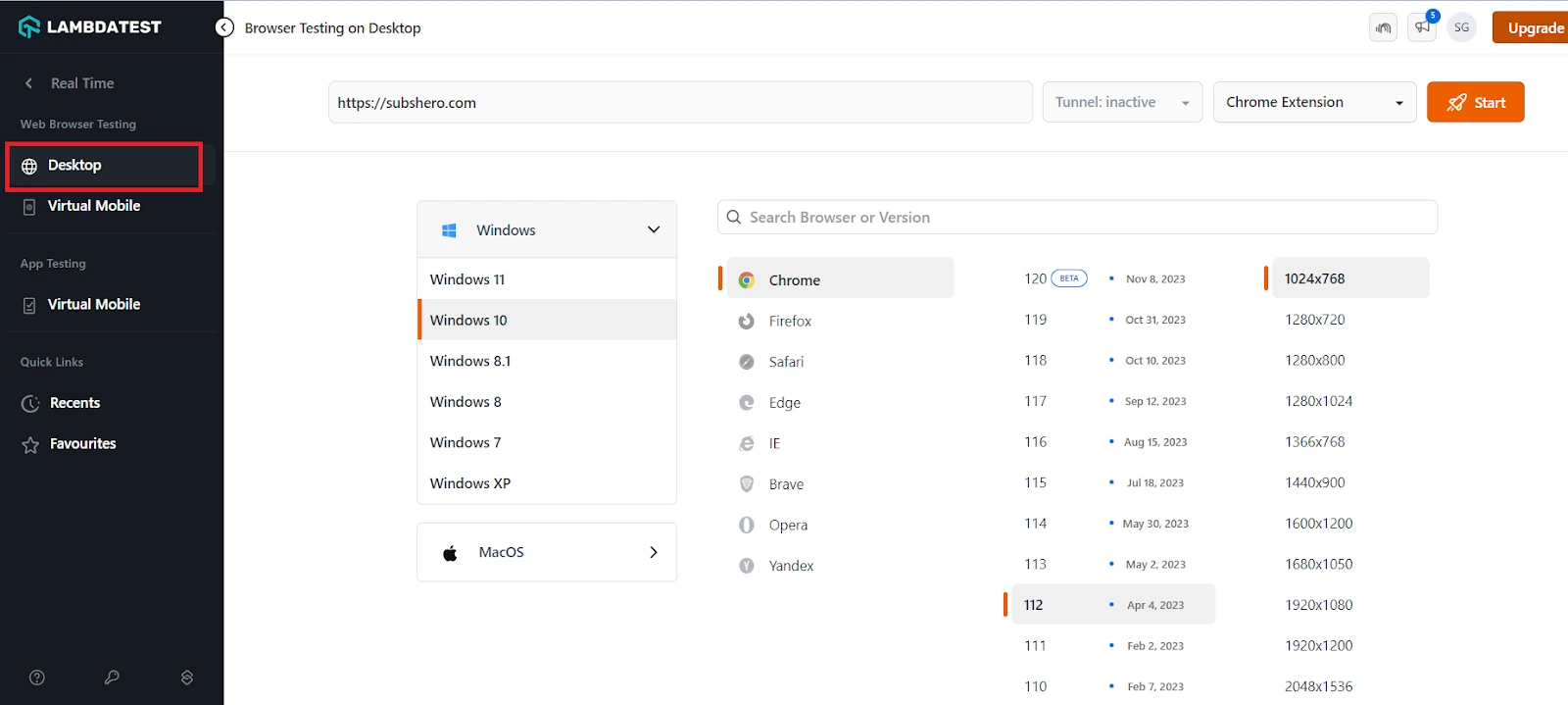
Step 4:Enter the URL you want to test, and then select the operating system, browser, browser version, and resolution from the given options.

Step 5:Click the Start button to launch your test.
It will launch a cloud-based machine, allowing you to perform web application testing based on your chosen test configuration.
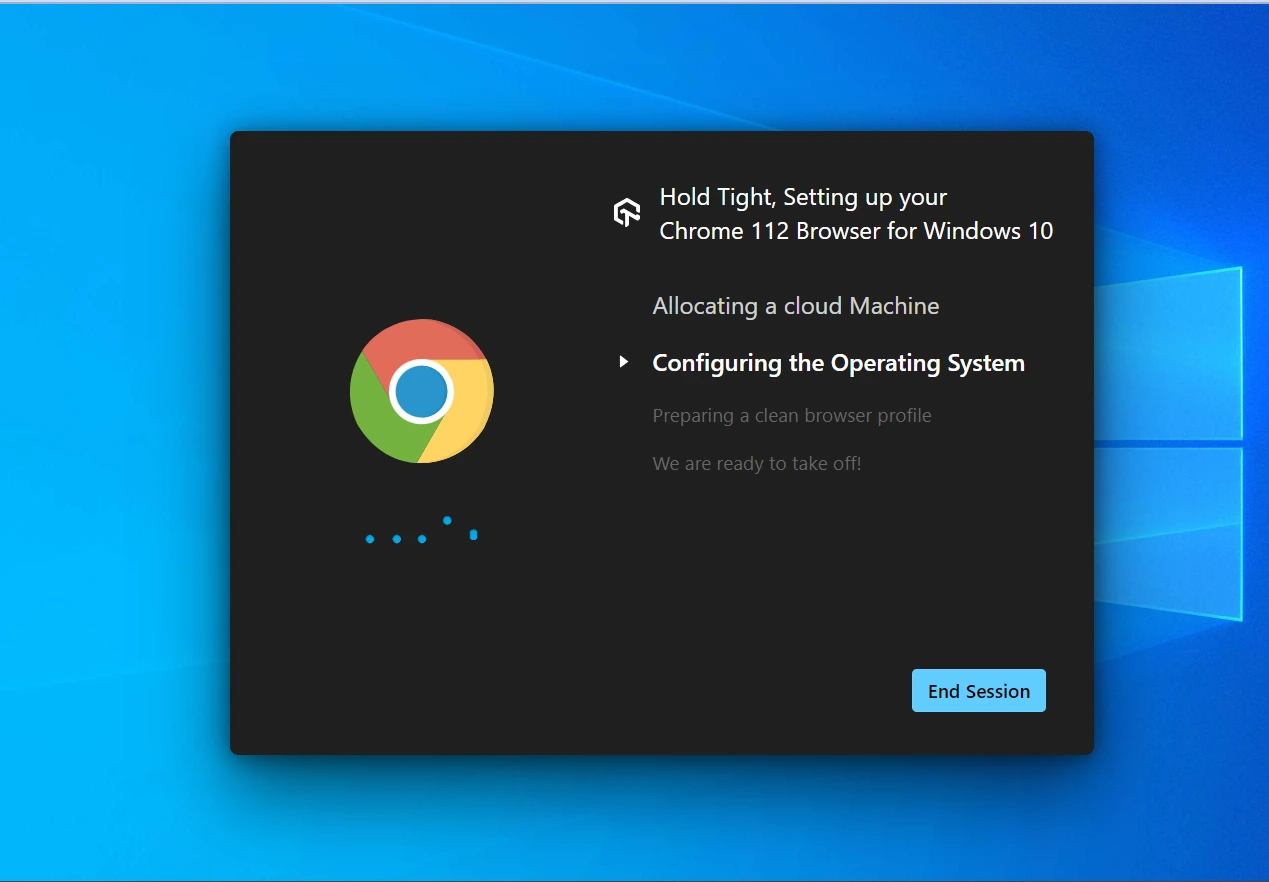
You can perform any necessary actions from the left menu options. For example, you can click the Record Session button to record and share the entire test process with your team. You can also capture screenshots, change the browser, version of the browser, and resolution as per your requirement on the go, and more.

You can perform manual testing on a virtual mobile as well. To do so, you need to follow the steps given below.
Step 1: Log in to LambdaTest as explained above.
Step 2: Click Real Time from the left menu.
Step 3:Click Virtual Mobile under Web Browser Testing.

Step 4:Enter the URL, then select Android or iOS based on your preference, browser, device, and the device version.
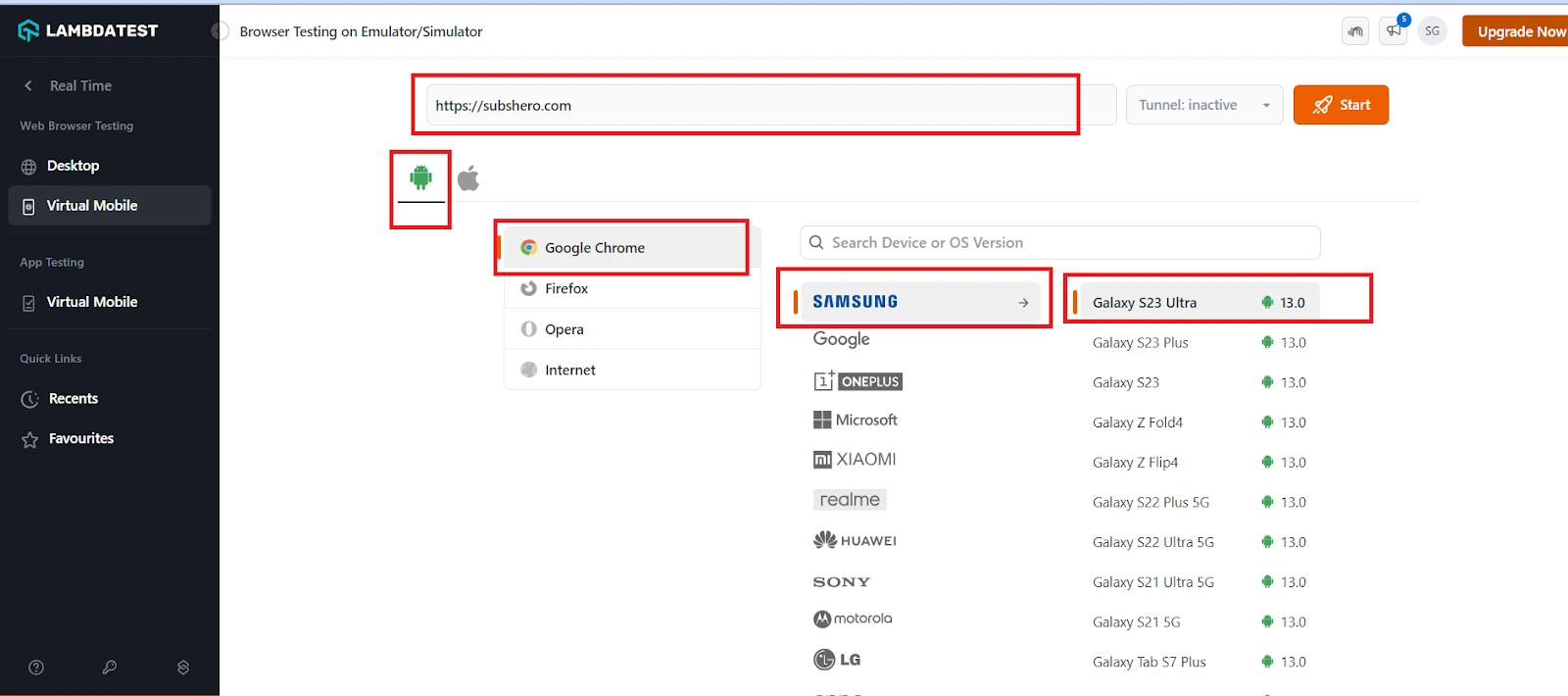
Step 5:Click the Start button once you set your configuration.
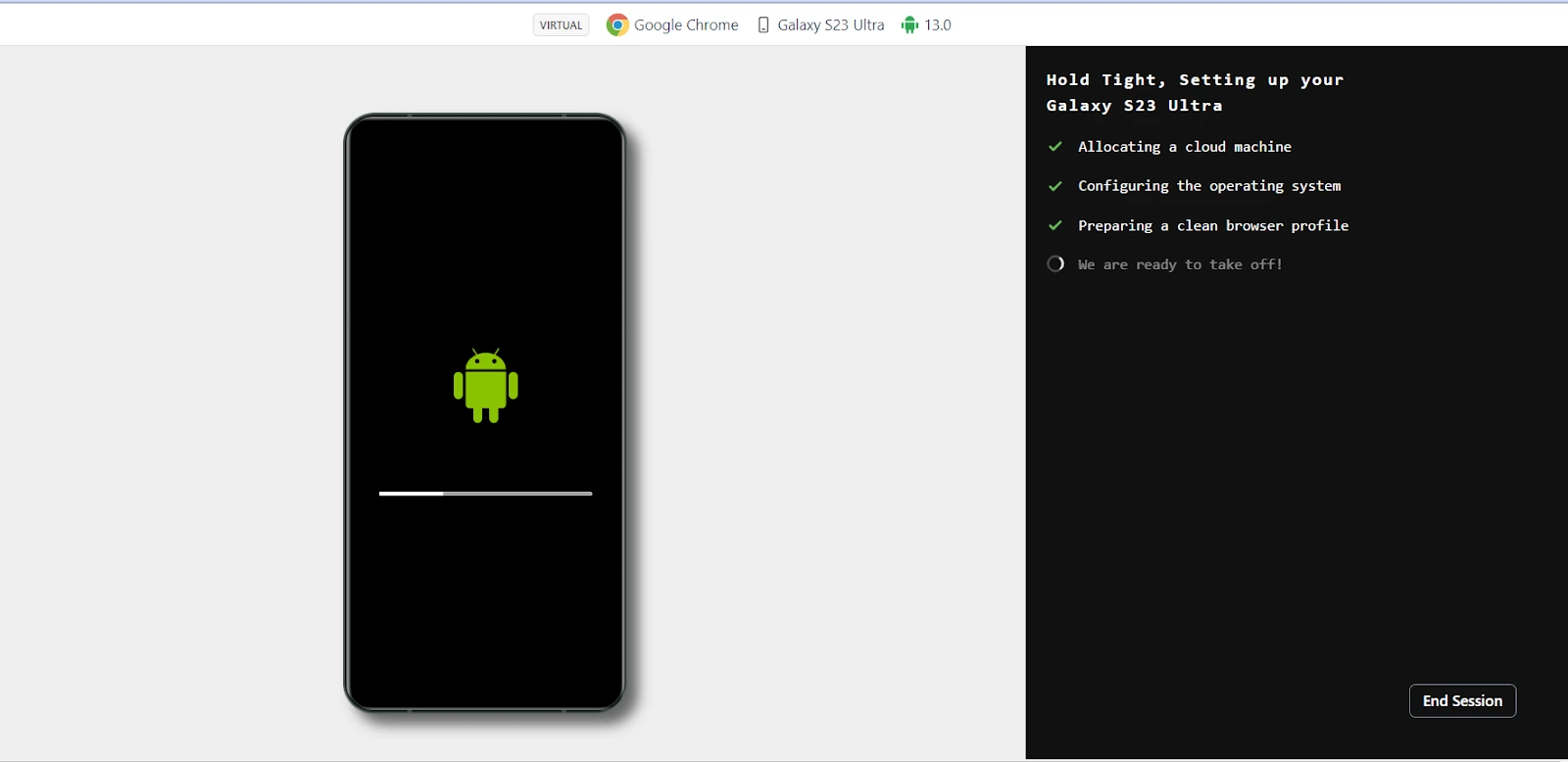
It will launch the website you entered with virtual device infrastructure. Now, you can perform your test.
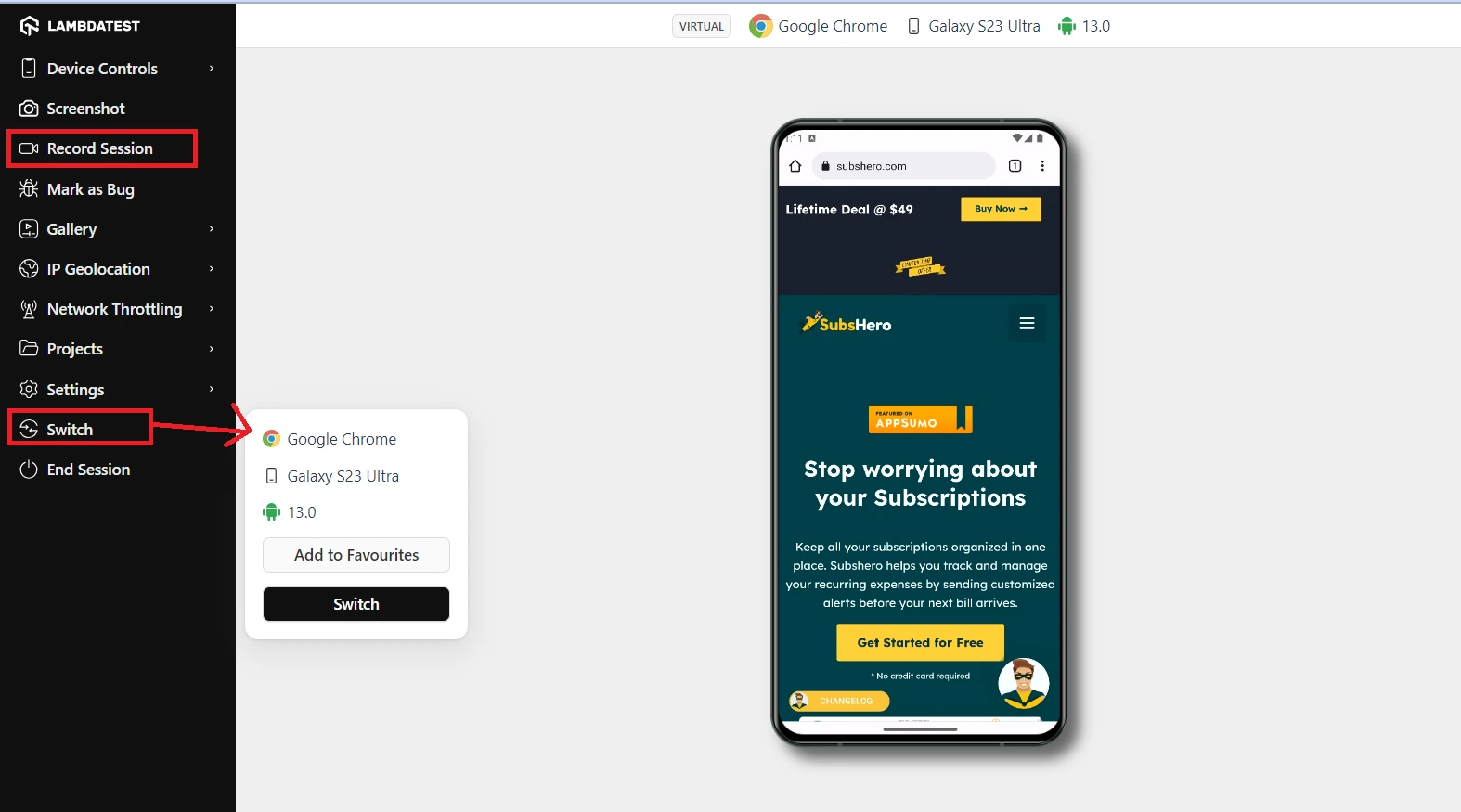
You can perform any necessary actions from the left menu options. For example, you can click on the Device Controls option to control the volume and brightness of your virtual mobile.
You can also record the testing process by clicking the Record Session button and sharing it with your team. You can also capture screenshots, change the browser, version of the browser, and resolution as per your requirement on the go, and more.
Now that you have seen how you can perform real-time testing using a browser and virtual mobile, in the following section, let us know how you can perform automation testing for web application testing.
This section will look into the steps required to run your automation test over the LambdaTest platform. To do so, you must first set up some capabilities to build a bridge between your cloud platform and your local test script. By following the steps below, you can easily set up those capabilities.
Step 1: Log in to LambdaTest as explained above.
Step 2: Get your Username and Access Key by going to your Profile avatar from the LambdaTest dashboard and selecting Account Settings from the list of options.
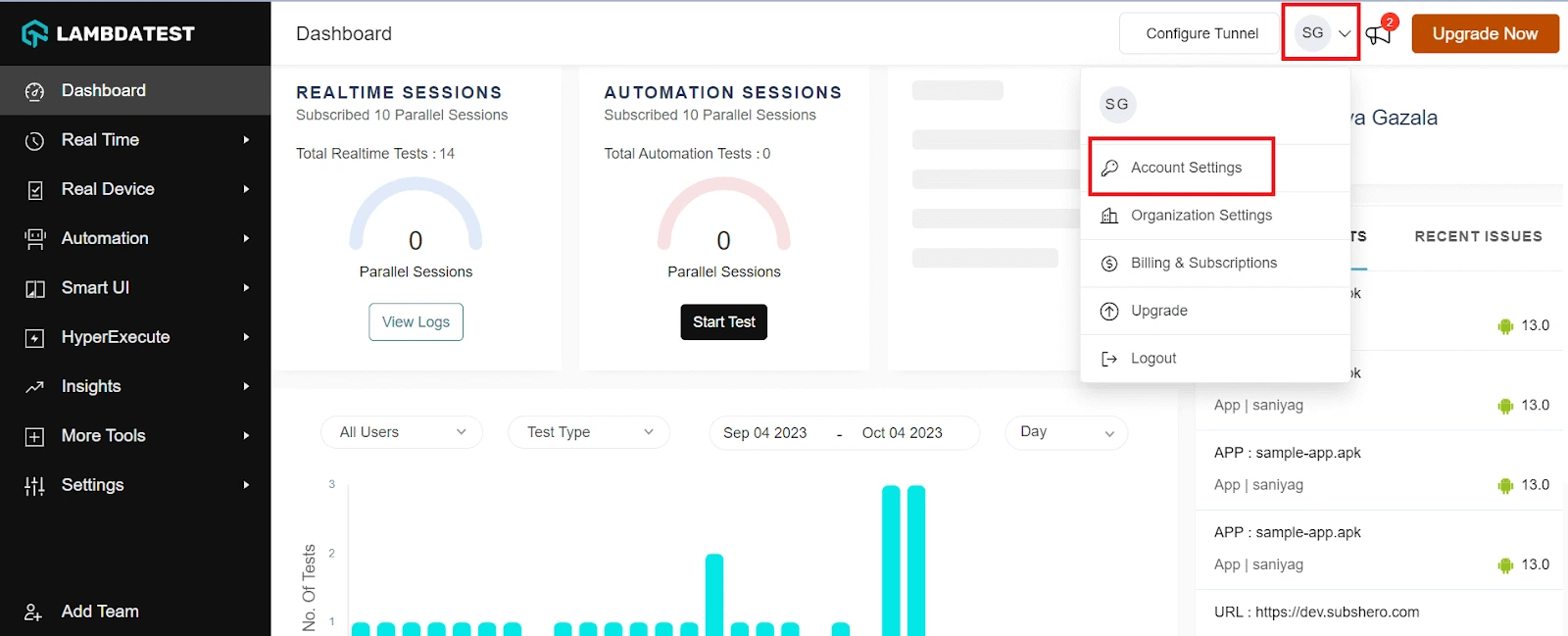
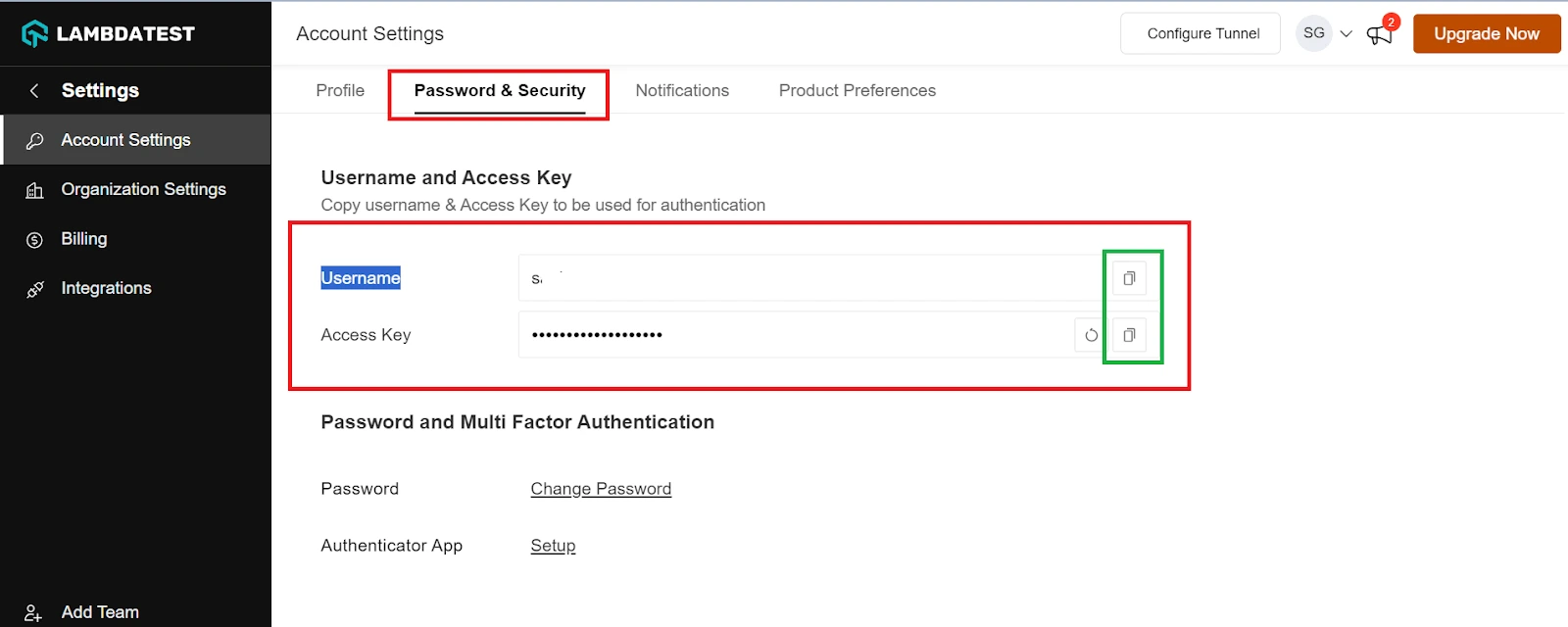
Step 3: Copy your Username and Access Key from the Password & Security tab.
Step 4:Generate Capabilities containing details like your desired browser and its various operating systems from the LambdaTest Capabilities Generator as per your requirement.
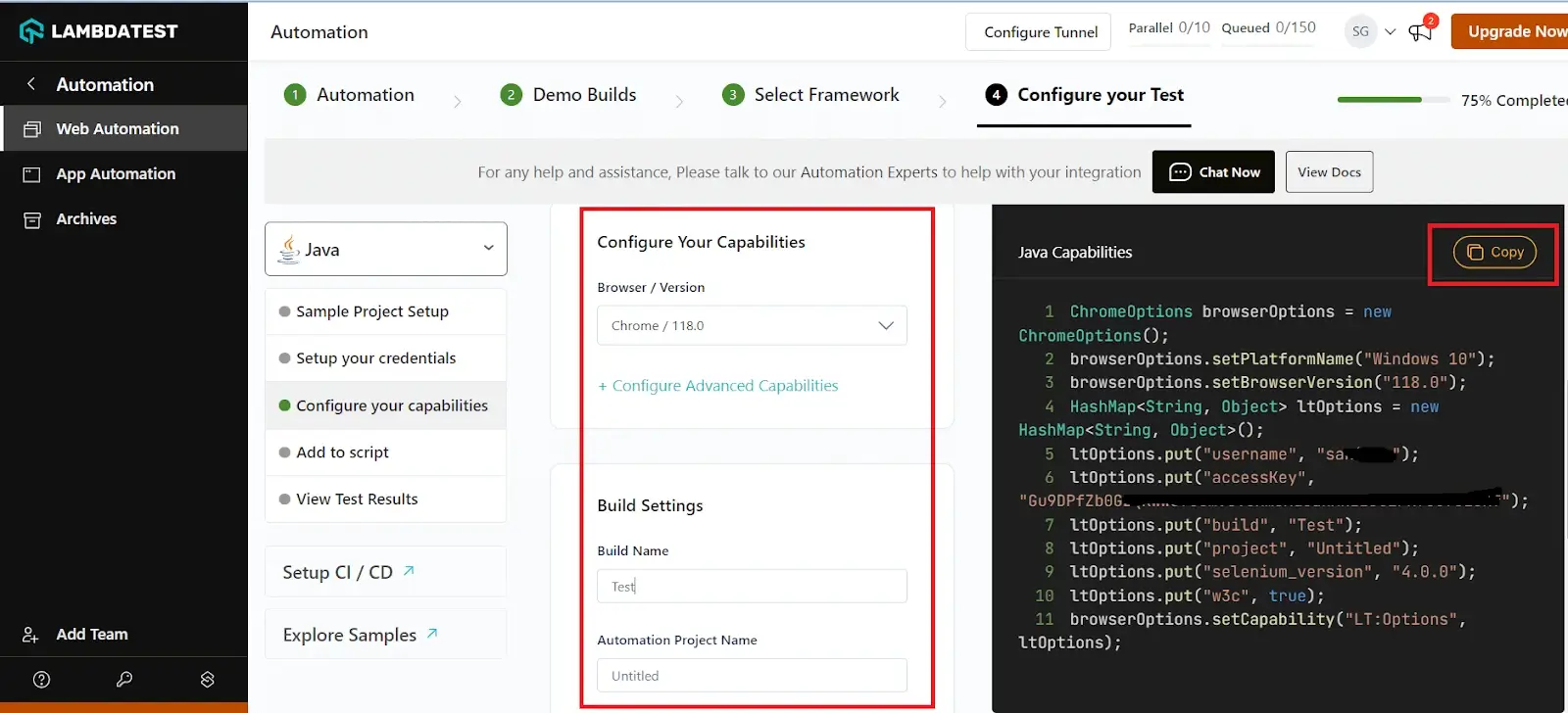
Step 5: Now that you have both the Username, Access key, and capabilities copied, all you need to do is paste it into your test script.
Note: These capabilities will differ for each programming language and testing framework you choose.
To understand conducting tests on LambdaTest using any programming language and testing framework, refer to the comprehensive guidance provided in the LambdaTest support documentation. This resource will provide a complete guide and purposeful insights into running tests effectively.
Now that you have seen all the benefits, approaches, web application testing, and how you can automate web application testing over the cloud. In the following section, let us see some challenges in web application testing.
In web application testing, there are specific challenges that most developers and testers encounter and find difficult to address. This may lead to failure in completing web app testing, and the quality of the application may be affected. Hence, it is of utmost importance to be aware of the challenges of web application testing.
Uncontrolled web app environments: Web applications run on various platforms, screen resolutions, browsers, and devices, making it difficult to achieve comprehensive test coverage across all environments. Testers must carefully evaluate and prioritize the most relevant combinations for testing based on user demographics and usage patterns.
Frequent UI change:Web applications undergo regular updates, introducing new features, third-party integrations, or modifications to the user interface. Keeping up with these changes can be challenging for testers, as it requires maintaining and updating test scripts to align with the evolving UI, ensuring proper test coverage, and avoiding script failures.
Handling image comparisons: Web automation often involves comparing images for visual validations. Managing image comparisons can be complex, as variations in pixel details, such as shape, size, and color, must be carefully handled to ensure accurate and reliable image conversions for testing purposes.
Usability issues:Usability problems can significantly impact the success of a web application. When multiple features are squeezed into a limited screen, usability can be affected. Testers must use proper usability testing tools and techniques to create comprehensive test plans focusing on seamless navigation, intuitive user interfaces, and meeting user expectations.
The challenges mentioned above in web application testing can be mitigated by following the below best practices.
Test on different browsers and devices
Perform web application testing on various browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge) and devices (desktop, mobile, and tablets). This ensures your application functions correctly and looks consistent across different platforms, providing a seamless user experience.
Test for scalability and load handling
Always perform scalability and load testing to assess your web application's performance under heavy user loads. Simulating high user traffic will help identify performance bottlenecks, such as slow page load times or crashes, and allow you to optimize your application's performance accordingly.
Perform security audits
You should conduct security audits to find vulnerabilities like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), or authentication flaws. Proper security measures, such as secure coding and encryption, are essential to protect your application and user data.
Implement continuous testing practices
Embrace continuous testing methodologies, such as continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD), to ensure your web application is continuously tested throughout the development lifecycle.
Validate user input and data handling: Thoroughly test user input fields, form submissions, and data handling processes to ensure data integrity and prevent common issues like data loss, incorrect calculations, or validation errors. Validate input against expected formats, perform boundary value analysis, and handle error conditions gracefully.
Test for accessibility
Pay attention to web accessibility standards and guidelines, such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), to ensure that your web application is accessible to impaired users. Test for screen reader compatibility, keyboard navigation, color contrast, and other accessibility features to provide an inclusive experience for all users.
By using various tools and platfrom like LambdaTest you can ehance accessibility testing. This platfrom allows you to leverage the Accessibility Automation feature that can help you streamline this process by integrating with Selenium and Cypress for automated accessibility testing. This feature ensures thorough coverage and adherence to accessibility standards.
For detailed guidance on using accessibility testing, refer to the support documentation on Accessibility Automation.
Monitor and analyze application performance
Continuously monitor your web application's performance using tools like Application Performance Monitoring (APM) or web analytics. Monitor key metrics such as response time, server load, and error rates to identify and proactively address performance bottlenecks.

Web app testing is crucial in ensuring web application's quality, functionality, and security. It helps to identify and rectify issues early in the development lifecycle, reducing the risk of costly bugs or vulnerabilities in production.
It ensures that the application functions as intended, provides a seamless user experience across platforms, and handles varying user loads effectively.
Organizations can deliver robust and reliable web applications by following best practices such as testing different browsers and devices, performing scalability and load testing, conducting regular security audits, and implementing continuous testing practices.
As technology evolves, web application testing must adapt to emerging trends and challenges, such as cloud infrastructure, mobile responsiveness, and the increasing complexity of web applications. Organizations can continuously improve their web application testing processes and deliver high-quality applications that meet user expectations by staying updated with the latest testing methodologies, tools, and best practices.