
Learn the theory, components, and operation of AM transmitters, receivers, and superheterodyne receivers in analog communication. Understand the functions and classifications of radio receivers.

guillermoh + Follow
Download PresentationAn Image/Link below is provided (as is) to download presentation Download Policy: Content on the Website is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use and may not be sold / licensed / shared on other websites without getting consent from its author. Content is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use only. Download presentation by click this link. While downloading, if for some reason you are not able to download a presentation, the publisher may have deleted the file from their server. During download, if you can't get a presentation, the file might be deleted by the publisher.

EE 587 SoC Design & Test. Partha Pande School of EECS Washington State University pande@eecs.wsu.edu. SoC Test. Conceptual Architecture of Core Test. Three separate elements in the embedded core test infrastructure. Test pattern source and sink Test Access Mechanism
1.2k views • 38 slides

Test Taking Skills:. Training Category A. BEFORE THE TEST. WHAT YOU CAN DO BEFORE THE TEST TO IMPROVE TEST SCORES. WHAT CAN YOU DO BEFORE THE TEST?. Study for the test Develop a study plan Include self testing during your review Study in short periods
805 views • 26 slides

Test Anxiety. What is Test Anxiety?. If you experience test anxiety while taking a test you may notice the following: Mental distraction: your mind may drift while you are reading questions or writing answers, and you may have trouble concentrating on the test
2.37k views • 18 slides

This Is Only a Test: Managing Test Anxiety. What are the signs and causes of test anxiety? What can I do to prevent test anxiety? How should I prepare for tests? What should I do on test day? What if my mind goes blank? How do I cope with test anxiety? What should I do after the test?.
2.93k views • 16 slides

Test Development. stages. Test conceptualization defining the test Test construction Selecting a measurement scale Developing items Test tryout Item analysis Revising the test. 1. Test conceptualization. Defining the scope, purpose, and limits of the test.
4.83k views • 50 slides

8.3 t- test for a mean. T- Test. The t test is a statistical test for the mean of a population and is used when the population is normally or approximately normally distributed and is unknown . The formula for the t test is The degrees of freedom are d.f. = n – 1.
383 views • 11 slides

Dynamic Testing. Test Design Techniques. Dynamic Testing. Testing that involves the execution of the software of the component or system Execution of the test object on a computer Need a test bed. Test Bed. Test Driver. Test Case 1. Test Case 2. Test Case n. Stub1. PoC. Test
1.46k views • 46 slides

EMC WRF Developmental Test Center, NASA/ NOAA/DoD Joint Center for Satellite Data Assimilation CPC Climate Test Bed NHC Joint Hurricane Test Bed HPC Hydrometeorological Test Bed SPC Hazardous Weather Test Bed with NSSL SWPC Space Weather Prediction Test Bed with AFWA
522 views • 17 slides

Marketing Mix Test. This test consists of 10 questions designed to test your understanding of methods of budgeting The links provide you with a choice of answer, along with explanations and solutions. You will need a calculator to complete this test. Question 1. B2B is a method of?
662 views • 40 slides

Test Case. Introduction. Purpose: Writing Test Case Attendees: Testers Duration: 2 hours. Objectives. After the course, student will be able to: Understanding the way to create a Test Case Using Test Case checklist to review a Test Case. Agenda. Design test case Write test case
1.28k views • 26 slides

55. 60. 50. 5. 45. 10. 40. 15. 35. 20. 30. 25. TEST. TEST. TEST. TEST. TEAM. TEST. Active Learning. in the College Classroom. Open Letter. Five on Friday. Five on Friday. Fri. Sun. Mon. Tue. Wed. Thu. Sat. Three Before Me. Focused Listing. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
793 views • 29 slides

This Is Only a Test: Managing Test Anxiety. What are the signs and causes of test anxiety? What can I do to prevent test anxiety? How should I prepare for tests? What should I do on test day? What if my mind goes blank? How do I cope with test anxiety? What should I do after the test?.
775 views • 16 slides
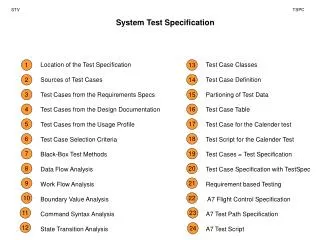
STV. TSPC. System Test Specification. Location of the Test Specification Sources of Test Cases Test Cases from the Requirements Specs Test Cases from the Design Documentation Test Cases from the Usage Profile Test Case Selection Criteria Black-Box Test Methods Data Flow Analysis
775 views • 26 slides

Test Taking Strategies, Test Preparation and Reducing Test Anxiety. Learning Assistance Center (LAC) University Pavilion, Suite 120 556-3244. Relax. Look at the test. Read the directions When you are stuck, move on!. Ask for clarification Learn from the test.
659 views • 10 slides

Power of 1. Where the Money Comes From. Back End Leadership. Front End Distributor. Middle Executive. TEST. TEST. EX. EX. TEST. You =. You =. You. TEST. TEST. 1. 12. 2. 4. 6. 8. TEST. TEST. Blue Diamond. Diamond. Gold. Lapis. Ruby. Emerald. 30% Retail 6-14% on
583 views • 11 slides

Sign Test and Run Test. Raymond L. Tremblay. BioConservaci ó n. Biol 4037 LWV 12:30-1:20. Los temas. Regresión Lineal Comparando ecuaciones lineales Bondad de ajuste (Chi square) Tabla de contingencia The sign test (la prueba de signos) p 538 The run test (la prueba de corrida) p 584.
450 views • 11 slides

Test Security. Resources New to Test Security Highlights. Test Security Resources. Test Security: http://www.tea.state.tx.us/student.assessment/security/ 2012 Test Security Supplement Launch of Web-based Texas Test Administrator Online Training Modules. New to Test Security.
2.49k views • 15 slides

Warm up. How would you define a double replacement reaction?. Warm up answers. A chemical reaction in which the ions of the reactants switch partners to form products. TEST TEST TEST TEST TEST TEST TEST.
457 views • 10 slides

Chi-square test or c 2 test. What if we are interested in seeing if my “ crazy ” dice are considered “ fair ” ? What can I do?. Chi-square test. Used to test the counts of categorical data Three types Goodness of fit (univariate) Independence (bivariate)
837 views • 29 slides

Test Plan- 46 Test Wing. Test Title: Interoperability with Firebird UAV Plan #: 46/JRATS/002-004 Test Sponsor: PM, JRATS UGV Date: Test Article: JUGV, EDM #4 Serial No: EDM01-0004 Test Officer: Capt Merryman Test Duration: 2 hours 24.5 minutes Range: B-75. Introduction.
2.05k views • 1 slides